[ad_1]
NEW DELHI: Mystery has always surrounded how the mossy region on the Sun interlinks with its lower atmospheric layers and undergoes a remarkable heating process from 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit to nearly 1 million degrees Fahrenheit which is 100 times hotter than the adjacent bright surface. Recent research, led by scientist Souvik Bose, has shed light on the superheating mechanism at work within the moss.
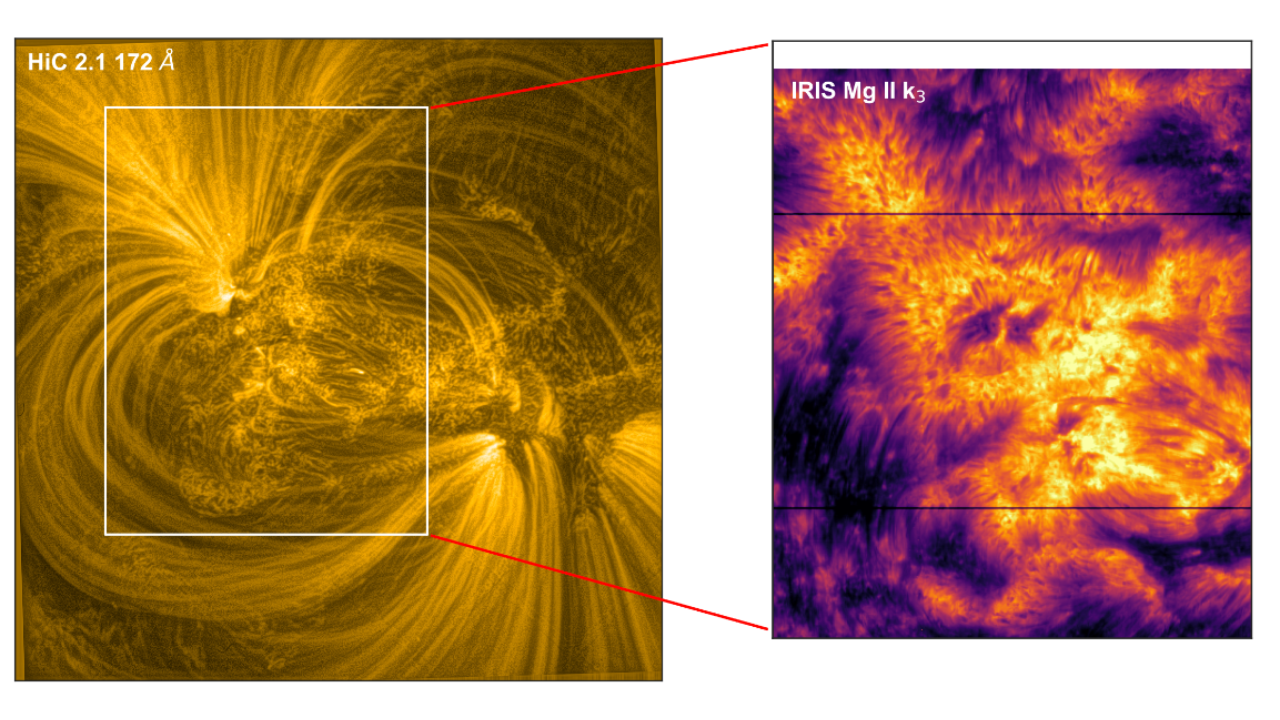
The research has utilised the data collected from Nasa‘s High Resolution Coronal Imager (Hi-C) sounding rocket and the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) mission, coupled with intricate 3D simulations, to unveil the potential role of electrical currents in the heating process.
Within this region lies a complex web of magnetic field lines, akin to invisible threads of spaghetti. This magnetic entanglement generates electrical currents, contributing to the heating of materials across a broad temperature spectrum, ranging from 10,000 to 1 million degrees Fahrenheit. This localized heating in the moss appears supplementary to the heat emanating from the scorching, multi-million-degree corona situated above. These findings, detailed in the journal Nature Astronomy on April 15, offer crucial insights into understanding why the Sun’s corona surpasses the surface temperature.
“Thanks to the high-resolution observations and our advanced numerical simulations, we’re able to figure out part of this mystery that’s stumped us for the past quarter of a century,” remarked author Souvik Bose, a research scientist at Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory and Bay Area Environmental Institute, Nasa’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley. “However, this is just a piece of the puzzle; it doesn’t solve the whole problem.”
Further opportunities to unravel the complete mystery are on the horizon: Hi-C is slated for another launch this month to capture a solar flare, potentially including another moss region alongside IRIS. Yet, to garner observations comprehensive enough to elucidate how the corona and moss undergo heating, scientists and engineers are actively developing new instruments for the future MUlti-slit Solar Explorer (MUSE) mission.
A small-scale, bright, patchy structure composed of plasma in the solar atmosphere bears a striking resemblance to earthly plants, leading scientists to dub it “moss.” This moss was initially discovered in 1999 by Nasa’s TRACE mission. It predominantly forms around the center of sunspot groups, where magnetic conditions are robust.
The research has utilised the data collected from Nasa‘s High Resolution Coronal Imager (Hi-C) sounding rocket and the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) mission, coupled with intricate 3D simulations, to unveil the potential role of electrical currents in the heating process.
Within this region lies a complex web of magnetic field lines, akin to invisible threads of spaghetti. This magnetic entanglement generates electrical currents, contributing to the heating of materials across a broad temperature spectrum, ranging from 10,000 to 1 million degrees Fahrenheit. This localized heating in the moss appears supplementary to the heat emanating from the scorching, multi-million-degree corona situated above. These findings, detailed in the journal Nature Astronomy on April 15, offer crucial insights into understanding why the Sun’s corona surpasses the surface temperature.
“Thanks to the high-resolution observations and our advanced numerical simulations, we’re able to figure out part of this mystery that’s stumped us for the past quarter of a century,” remarked author Souvik Bose, a research scientist at Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory and Bay Area Environmental Institute, Nasa’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley. “However, this is just a piece of the puzzle; it doesn’t solve the whole problem.”
Further opportunities to unravel the complete mystery are on the horizon: Hi-C is slated for another launch this month to capture a solar flare, potentially including another moss region alongside IRIS. Yet, to garner observations comprehensive enough to elucidate how the corona and moss undergo heating, scientists and engineers are actively developing new instruments for the future MUlti-slit Solar Explorer (MUSE) mission.
A small-scale, bright, patchy structure composed of plasma in the solar atmosphere bears a striking resemblance to earthly plants, leading scientists to dub it “moss.” This moss was initially discovered in 1999 by Nasa’s TRACE mission. It predominantly forms around the center of sunspot groups, where magnetic conditions are robust.
[ad_2]
Source link